Out of range liquidity happens when the current price of a pool moves outside of the positions set price range due to swap activity. Additionally, liquidity providers can add liquidity out of range. They do this by setting their positions a price range above or below the current price in a pool.
We had our first liquidity pool out of range!
A “liquidity pool out of range” means that the current market price of an asset in a decentralized exchange (DEX) liquidity pool has moved beyond the price range that a liquidity provider (LP) has set for their deposited funds, rendering their liquidity inactive and preventing them from earning fees on swaps occurring outside that price range.
Out of Range below
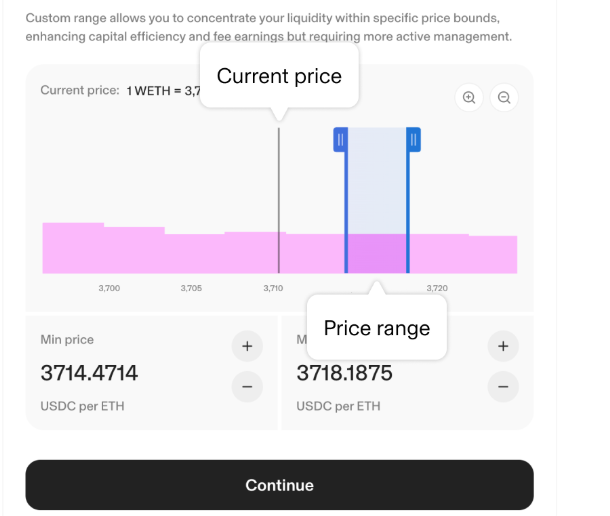
Out of range over
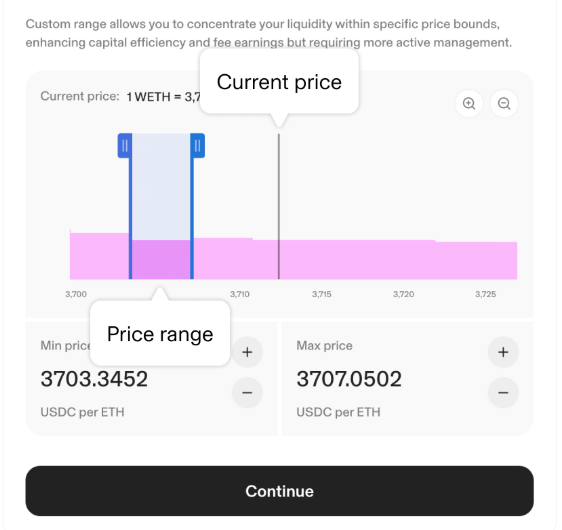
Key points about “liquidity pool out of range”:
- Concentrated Liquidity:This issue is most relevant when using “concentrated liquidity” strategies, where LPs specify a narrow price range to maximize yield, but if the price moves significantly outside this range, their liquidity becomes unusable.
- Impact on Earning Fees:When a pool is out of range, the LP will not earn any fees from swaps occurring outside their specified price range.
- How to Fix: To regain active liquidity, the LP needs to adjust their price range by withdrawing their funds from the pool and re-depositing them with a new, wider price range that encompasses the current market price.


Leave a Reply